 An analysis of the historical evolution that has presented the treatment of this type of surfaces around the world.
An analysis of the historical evolution that has presented the treatment of this type of surfaces around the world.
by Luis Carlos Franco Granada*
In the last 20 years, one of the largest technological transformations in the metal surface treatment industry before painting has been taking place; where only phosphate-based surface conversion systems were available. The evolution of phosphate treatment systems only proposed iron phosphates and zinc phosphates as an innovation. Later, modifications such as Zinc-Nickel, Zinc-Manganese, Tri-cationic, Modified with Calcium, among others, appeared.
Although phosphate technology has accompanied us for many years and the usefulness as protection of the metal surface before painting has been reliable, there are some deficiencies associated with the following:
1. Chemical technology: Phosphates as a chemical mechanism require the following:
1.1 Internal accelerants, external accelerants that favor an infinite number of secondary chemical reactions whose side effects cause systems to repeatedly lose chemical control, including environmental impact with the production of nitrous gases.
1.2 By chemical kinetics, phosphates produce sludge, associated with the production of insoluble tertiary phosphates in the medium, which go to the bottom of the tank. It is estimated that at least 50% of soluble phosphate is converted into sludge, which must be disposed of according to environmental standards.
1.3 In general, phosphates require certain temperature ranges that guarantee greater speed in the conformation of the phosphate film on the surface.
1.4 Reaction times are part of the control variables, thus obtaining the appropriate layer thicknesses for good corrosion protection before painting.
1.5 Within the design variables of the phosphating plants, the volume ratio of the phosphating solution per unit area of the parts to be treated must be considered. This involves the design of large tanks to store the required solution that meets chemical kinetics.
2. Environmental performance: The environmental performance of phosphates has been questioned due to the resources it requires, among which are:
2.1 Water resource: Systems based on zinc phosphates are very demanding of fresh water of good quality, which is used to rinse the pieces after the stages of degreasing, chemical pickling, phosphate, passivation, among others. Normally the rinsing stages require constant overflow, which implies consumption of large volumes. The quality in the discharge of the water from rinses is very varied, since it can have deviations that require its treatment such as: Very low or very high pH ranges, according to the stage; heavy metals such as Zn, Cr, Pb, among others; contents of surfactants, fats and oils. Generally speaking, the water used for rinsing requires treatment to comply with the regulations.
2.2 Energy resource: Phosphate technology traditionally requires energy for heating the degreasing stages at temperatures up to 70 0C and the phosphate stage 50-55 0C. This energy can be obtained by fossil fuels, which produce as a side effect, pollution to the environment by greenhouse gases.
2.3 Soil resource: Phosphate technology produces large amounts of sludge, as a result of fats accumulated in the degreasing stages and sludge caused by the chemical reaction of phosphating. These must be treated as hazardous waste, which require special treatment according to the regulations.
New technologies
Surface treatment technology has taken a big leap with options other than phosphates, which in synergy with degreasers free of strong alkalinities and strong acidities, manage to form reliable systems, with excellent performance as a pre-paint layer. Among the offers in the market in new technologies, Oxsylan Technology stands out, which has the following characteristics:
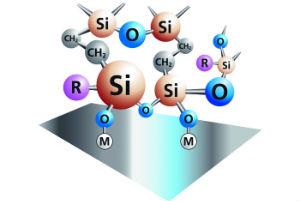
1. Definition: From the Oxsylan technology, a product is part that has the function of replacing the chemical conversion made by phosphates, but using certain polymers of Silanes, which protect the metal surface before painting, in a similar way as phosphates do, but with the following differences:
1.1 The polymeric conversion film on the surface of the metal is at the nano level, requiring product consumption of less than 0.1 g/m2 of surface to be treated.
1.2 This treatment stage works at room temperature. Therefore, it does not require energy consumption.
1.3 Contact times are very low (approximately 15 to 30 seconds). The above, because in the conversion stage no chemical reaction occurs; polymerization actually occurs in the later stages of drying.
1.4 This technology handles references that do not require subsequent rinses. This decreases water consumption.
1.5 The Oxsylan stage does not produce sludge, compared to phosphates where the conversion stage is the one that generates the most sludge, of the entire system.
2. Degreaser technology: To get the most out of Oxsylane technology, it is necessary to combine it with a good technological option for the degreasing stage. In the degreasing stages, products with the following characteristics are being handled compared to traditional degreasers:
2.1 Degreasers based on modern surfactants of easy rinsability, avoiding traditional products of alkalinity or strong acidity.
2.2 Degreasers with low or non-low temperature requirements. This leads to low energy consumption.
2.3 Reduction of water consumption in the rinsing of the degreased parts, due to the efficiency of the degreasing and its low residuality on the piece.
2.4 Reduction of contact times in the degreasing stages due to their efficiency.
2.5 Low sludge production compared to traditional degreasers, reducing the environmental impact on its disposal.
3. Resource consumption of Oxsylan technology:
3.1 Reduction of water consumption by up to 60% compared to traditional zinc phosphate systems.
3.2 Decrease in sludge production by up to 80% compared to traditional Zinc phosphate systems.
3.3 Reduction of energy consumption of up to 60% compared to traditional Zinc phosphate systems.
3.4 Increased productivity of up to 40% compared to traditional Zinc phosphate systems.
3.5 In environmental requirements: With an Oxsylan system it is possible to comply even with resolution 0631 of 2015 of the Ministry of the Environment of Colombia, without requiring the implementation of wastewater treatment plants.
* Luis Carlos Franco Granada is a Chemical Engineer from the National University of Colombia with 24 years of experience in the field of pre-painting metal surface treatment in the areas of formulation and application. Specialist in Germany in Environmental Management Systems for Industry. Specialist in the application of new surface treatment technologies such as nanotechnology in one of the most advanced multinational companies in the development of these technological solutions for this type of industry. He currently serves as Commercial and Technical Director of the Surface Treatment Division of one of the most recognized companies in this sector. You can contact him via email [email protected] - [email protected] or by calling him +57 312-7771173























Leave your comment