 We continue in this second part the analysis on pigmentary system, dispersion polymers and the relationship between the two, with the aim of highlighting obvious but not always understood particularities.
We continue in this second part the analysis on pigmentary system, dispersion polymers and the relationship between the two, with the aim of highlighting obvious but not always understood particularities.
by Jordi Calvo Carbonell*
In the first part of this article we talked about how polymers are obtained in paints and what kind of characteristics have the most used in our sector. In addition, the way in which coalescence occurs was explained in a general way.
The issue of coalescence in the presence of solid particles will now be addressed.
The pigmentary system formed by pigments and charges constitute in the paint film a network of solid particles of very variable size. The particle size of titanium dioxide is about 0.2 microns while charges can range from 2 to 20 microns in the case of calcium carbonate. To facilitate the exposure we will stick to these two components ignoring others in a laminar way such as talc, kaolin or mica.
When it is said that a calcium carbonate has a particle size of 10 microns it is indicating that this is the cut size of the particle, the reality is that the particles of this charge have a Gaussian distribution in which mostly the particle size is close to 10 microns however there is an important part of particles of smaller size.
The particle size of polymer dispersions is 0.05 to 0.8 microns and is also represented by a Gauss bell as there is a particle size distribution around the nominal value.
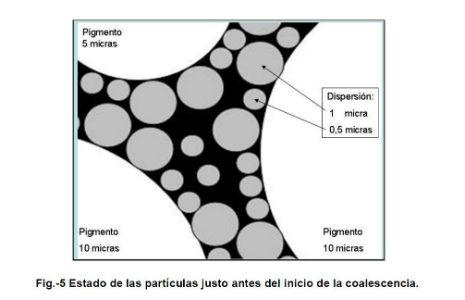
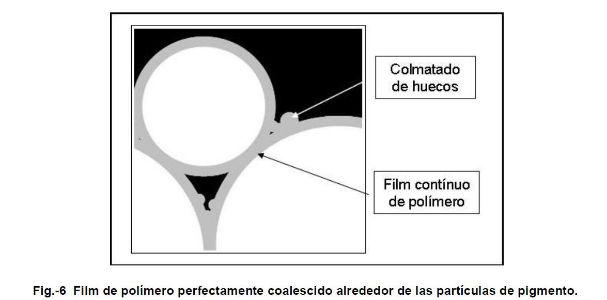
During the manufacturing and storage process the polymer particles, inside their micelles, tend to adhere on the particles of the pigment system due to the characteristics of the surfactants, in the micelle the lipophilic terminals are oriented towards the center coming into contact with the polymer while the hydrophilic terminals remain on the outside and tend to join with the particles of the pigment system. This means that in a paint, pvc In fig.-4 you can see what has been exposed so far. A heterogeneous pigmentary system in terms of particle size and the arrangement of polymer dispersion particles. Fig.-4 Distribution of pigment and polymer in paint As the process of evaporation of the continuous medium, water, progresses, the particles approach each other, see Fig.-5, so that when the PVC (Pigment Volume Concentration) is equal to or lower than the CPVC (Critical Pigment Volume Concentration) the pigment is wrapped in polymer dispersion particles and even some of these are distributed in the continuous medium without having contact with the others. Fig.-5 State of the particles just before the start of coalescence. Upon contact the dispersion particles are deformed, as much as the softening produced by the coalescing or by the thickness of the soft polymer in the case of Core-Shell or sequential polymers allows them, this produces a rapprochement between the pigment particles and the formation of a polymer film around them, see fig.-6. Fig.-6 Polymer film perfectly coalesced around the pigment particles. As the evaporation of the water contained in the film occurs, the polymer particles that are not adhered to the pigment particles tend to coalesce with each other before coming into contact with them, the vacuum effect sucks into the holes the loose particles, or the aggregates of these, which produces a filling of the holes with the possibility of leaving empty spaces inside the film. This possibility is all the more likely the harder the core of the particle, apparently in the previous section the ease of penetration is higher in soft or sequential polymers. The particle size of the pigment system, its effect on PVCC Table 1 shows the CPVC's calculated from the Oil Absorption Index (OAI) of calcium carbonates with cutting sizes of 20, 10 and 3 microns respectively. Table-1 Comparison of PVCC according to particle size. It is clearly observed that as the particle size of the pigment system is reduced, the value of the CPVC is reduced with the consequences that this entails: Loss of wet rubbing, mud-cracking, excessive water permeability, color problems in the patching, resistance to the outside, etc. From the above, it is concluded that the larger the particle size of the pigment system, the higher the CPVC value due to the lower need for binder to coat all pigment particles. Final Notes In outdoor paints the PVC of the paint must be placed at values close to the CPVC in order to ensure the impermeability of the paint film in order to protect the substrate and prevent the penetration of water through it. with this objective and to obtain an adequate economic balance it is preferable that the PVC is between 5 and 10 points above the PVCC in order for the polymer to form a continuous film capable of producing waterproofing and in turn avoiding the mud-craking problems that occur in the CPVC. In interior paints the PVC must be as high as allow the performance that the paint must meet so that the requirements of washability and acceptance of coloring pastes are met, these benefits are both lower the higher the PVC is compared to the CPVC. In general, as seen in the previous section the value of the CPVC lower when the particle size of the pigment system decreases and therefore the acceptance capacity of the loading material will be lower, this leads us to the conclusion that the particle size of the pigment system must be as high as the quality of the paint to be formulated in order to obtain good results. Technical. As for the choice of polymer, it has been seen that the thinner the dry polymer layer obtained, the greater its extension capacity and therefore the smaller amount of polymer is required to coat the pigment particles, thus producing a continuous binder film despite not filling all the gaps between particles and therefore ensuring the impermeability of the film. In the book "Manual of paints and plastic coatings" by Enrique Schweigger reference is made to a study by Holzinger presented in book XI of the Fatipec 143 congress (1972) in which the variation of the CPVC is indicated depending on the type of binder used, according to this work the CPVC in a paint based on a butyl-styrene acrylate polymer is located at 68% while the same formulation using a polymer of Vinyl acetate-butyl acrylate shows a CPVC of 63%. this confirms the importance of the particle size of the polymer dispersions since in the first case the particle size is 0.07 microns and in the second at 0.3 microns. The combination of both concepts would lead us to formulate with a pigmentary system formed by loads of 10 to 20 microns of cut size and with polymers of small particle size in order to obtain the best characteristics. The technician's mission is now to optimize both variables using loads of adequate size that provide sufficient covering power but that minimally increase the value of CPVC and polymers of small particle size so that the minimum amount is required to wrap the entire pigment system. The choice of one and the other is part of the work of the formulating technician who must choose between conventional, core-shell or sequential dispersions depending on the required objectives. Page pick * Jordi Calvo Carbonell is a Chemical Engineer and can be contacted at the email [email protected]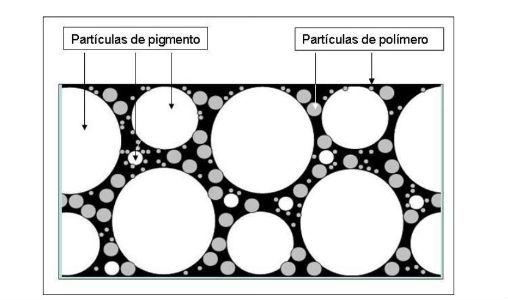
At present there is a certain tendency to use fine-sized loads in order to obtain a higher dry covering power, thus saving titanium dioxide. The question that arises is to what extent can this measure be abused? And how does this affect PVCC?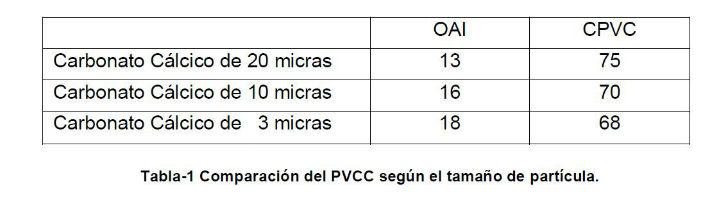
In the formulation of home and construction paints based on dispersion polymers, whether for interiors or exteriors, the value of the CPVC must be taken into account both from the point of view of performance and economic.
1 The Anglo-Saxon acronym is used because it is the most widely used.























Quedó atento